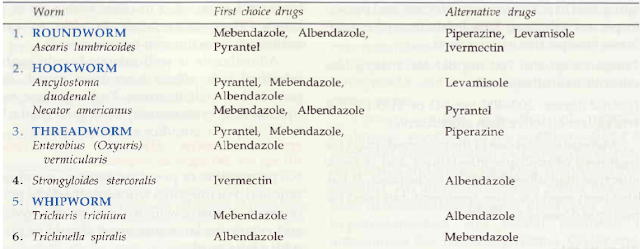
Anthelmintic
Anthelmintic
Definition:
Anthelmintics are drugs that either kill (vermicide) or expel (vermifuge) infesting helminths.
Helminthiasis is prevalent globally, but is more common in developing countries with poorer personal and environmental hygiene.
Helminthiasis is prevalent globally, but is more common in developing countries with poorer personal and environmental hygiene.
In the human body, GIT is the abode of many helminths, but some also live in tissues, or their Larvae migrate into tissues.
They harm the host:
1. By depriving him of food, causing blood loss, injury to organs, intestinal or lymphatic obstruction and by secreting toxins.
Helminthiasis is rarely fatal, but is a major cause of ill health.
Piperazine
It is used as an anthelmintic for treatment of pinworm and roundworm infestations.
It blocks the response of the ascaris muscle to acetylcholine causing flaccid paralysis in the worm, which dislodge from the intestinal wall and expelled in the faces.
The most important action of DEC appears to be alteration of Mf (microfilariae) membranes so that they are readily phagocytosed by tissue fixed monocytes, but not by circulating phagocytes. Muscular activity of the Mf and adult worms is also affected causing hyperpolarization due to the piperazine moiety, so that they are dislodged.
Thiabendazole
Mechanism of action:
Thiabendazole inhibits the helminth-specific enzyme fumarate reductase.
It is not known whether metal ions are involved or if the inhibition of the enzyme is related to thiabendazole’s anthelmintic effect.
Also arrest nematode cell division in metaphase by interfering with microtubule assembly.
Thiabendazole has broad-spectrum anthelmintic activity.
Mebendazole:
It is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic that is effective against a variety of nematode infestations.
It irreversibly blocks glucose uptake in susceptible helminths. thereby depleting glycogen stored in the parasite. It apparently does not affect glucose metabolism in the host. It also inhibits cell division.
It irreversibly blocks glucose uptake in susceptible helminths. thereby depleting glycogen stored in the parasite. It apparently does not affect glucose metabolism in the host. It also inhibits cell division.
Albendazole:
It is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic. Albendazole is widely used throughout the world for the treatment of intestinal nematode infection.
Niclosamide

The drug appears to act by inhibiting oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria and interfering with anaerobic generation of ATP by the tapeworm. Injured by niclosamide, the tapeworms are partly digested in the intestine.Bithionol
Bithionol has useful anthelmintic and has been used as a fasciolicide and taeniacide. It is still considered the agent of choice for the treatment of intestations caused by the liver fluke Fasciala hepatica and the lung fluke Paraganimus westermani.
Oxamniquine:
It has been shown to inhibit DNA, RNA and protein synthesis in schistosomes. It is available in capsules containing 250 mg of the drug.
Praziquantel
This novel anthelmintic has wide ranging activity against Schistosomeso, other trematodes, cestodes and their larval forms but not nematodes.
It is rapidly taken up by susceptible worms and appears to act by
causing leakage of intracellular calcium from the membranes contracture
and paralysis. The tapeworms lose grip of the intestinal mucosa and are
expelled
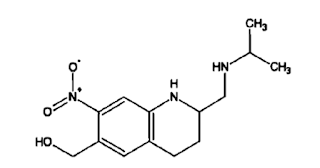
Ivermectin:

It is an extremely potent semisynthetic derivative of the antinematodal principle obtained from Streptomyces avermitilis.


























No comments: